Features of air conditioning in a house.
Originally designed to maintain a room or home cool, air conditioning has evolved and improved and now also functions as a fully-fledged heating system by utilizing heat pumps. However, it is not always easy to choose among the many different air conditioning options available on the market.
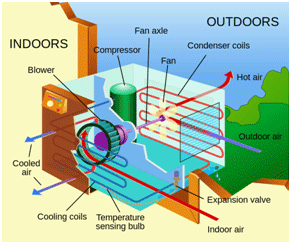
Before purchasing an air conditioning unit or system for your home, make sure you understand the different elements and models you can choose from:
- Inverter technology: operates the air conditioning appliance continuously and modulates the speed and power of the system according to the outside temperature and your heating/cooling needs. It can save up to 25% on energy consumption.
- Noise: technology has greatly reduced the noise of air conditioning. A good air conditioner produces less than 30dB of noise. Choose Energy Star approved products which are regulated for noise and energy consumption. There are also air conditioning units which have a silent option which produce almost no noise at all.
- Air filtration: contrary to popular belief, air conditioning improves air quality through its filters. The filtration quality is variable depending on the model and requires proper maintenance of the air conditioner.
- Installation tips: a poorly installed air conditioning system can cause cold drafts, when cold air is pushed towards the ceiling and then it descends back down again. Proper installation helps to mix cold air and room air together before being distributed. It is best to use a professional installer for optimal installation and performance.
- Power: an air conditioner will increase your electricity consumption related to a room between 15 and 25% typically, depending on usage. If the air conditioning unit is not powerful enough, it will go into overdrive, consuming more energy than necessary. In contrast, an over-sized unit will not increase your energy bill, but the unit may be unnecessarily expensive. To evaluate the correct power rating necessary to make a heat balance you should consult a professional installer.
Types of air conditioner.
There are different types of air conditioning units for the home; the most suitable will depend on whether you want to cool a single room or several rooms, your budget, the size of your home, and environmental factors, among other things.
- Monoblock: consists of a single unit, this device is suitable for small spaces. There are three versions: mobile, wall-mounted and window (built-in to a window).
- Split: more powerful and robust than the monoblock, they can be monosplit (an outdoor unit and an indoor unit) or multisplit (an outdoor unit and multiple indoor units to several rooms). Several versions are available:
- Mobile: easy to install, an immediate solution, but is often noisy. Suitable for occasional use.
- Wall-mounted: easy to install, it is aesthetic and compact.
- Console: floor-standing or attached to the bottom of a wall, it can be single or dual flow.
- Duct: ductwork connects the internal units together and the external unit is completely hidden in the ceiling. Only grilles are visible.
- Cassette: fixed to the ceiling, they are generally used for large spaces.
- Air Gas: reversible heat pump operating on natural gas.
- Solar air conditioning: reversible heat pump coupled with solar panels.
Hot and cold air conditioning.
2 in 1 systems are used for heating in the winter and cooling in the summer. However, reversibility is a secondary function of these devices: the heating is not as nice as that provided by a conventional radiator system.
Hot and cold, or dual, air conditioning is not generally considered to be a full heating system, but is effective as a supplementary heating source to:
- Air conditioning: the primary function of an air conditioning system is to cool. It can also be seen as an extra heating source because, from a technical point of view, it is a reversible air heat pump. It can reduce your electricity consumption. It returns an average of 3 kWh of heat for 1 kWh of energy used to run the compressor and the whole system works very efficiently. There is a disadvantage: this type of device can be noisy.
- Reversible heat pump: a heat pump draws heat contained outside and then transfers it inside the house. A reversible heat pump can reverse this cycle, to cool the interior. In practice, a reversible air pump is a reversible air-to-air heater. Heat pumps, whether of the air-water or water-water variety, are primarily designed to heat. They can serve as a cooling system, but not only for cooling itself. However, they are much more environmentally friendly and economical than traditional air conditioning.
